Bernoulli's Principle and its Applications
Bernoulli's Principle and its Applications: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Venturimeter,Speed of Efflux in Liquids,Application of Bernoulli's Theorem in Sprayer, etc.
Important Questions on Bernoulli's Principle and its Applications
Calculate the rate of flow of glycerine of density through the conical section of a pipe if the radii of its ends are and the pressure drop across its length is
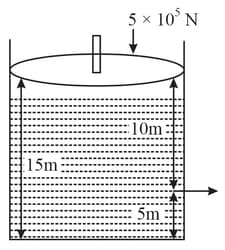
Consider a cylindrical tank of radius is filled with water. The top surface of water is at from the bottom of the cylinder. There is a hole on the wall of cylinder at a height of from the bottom. A force ofis applied on the top surface of water using a piston. The speed of efflux from the hole will be: (given atmospheric pressure, density of water , )
The venturi-meter works on :
Glycerin of density is flowing through the conical section of pipe. The area of cross-section of the pipe at its ends are and and pressure drop across its length is . The rate of flow of glycerine through the pipe is . The value of is _____.
The figure shows a liquid of given density flowing steadily in horizontal tube of varying cross-section. Cross-sectional areas at is and is if the speed of liquid at is then is
(Given and are liquid pressures at and points.
Density
and are on the axis of tube)
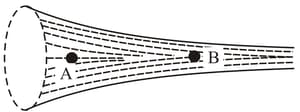
An ideal liquid is flowing through a pipe kept on horizontal floor as shown in figure. The flow is streamline flow. The pressure at two points are indicated, then
The vertical sections of four wings moving horizontally in air is shown in the options. In which case is the force upwards?
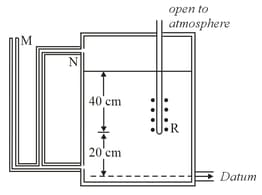
The tank in figure discharges water at constant rate for all water levels above the air inlet R. Find the height above datum to which water would rise in the manometer tubes M and N.
open to atmosphere
Water contained in a tank flows through an orifice of diameter , under a constant pressure difference of of water column. The rate of flow of water through the orifice is
Derive Bernoulli's theorem.
Figure shows how the stream of water emerging from a faucet "necks down" as it falls. Figure shows two levels separated by vertical distance . The cross-sectional areas and are marked in the figure. At what rate does the water flow from the tap?
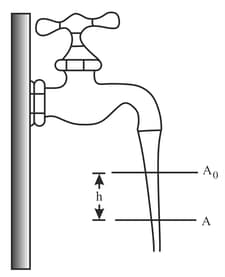
A large storage tank, open to the atmosphere at top and filled with water, develops a small hole in its side at a point below the water level. If the rate of flow from the hole is , then the diameter of the hole is [Take ]
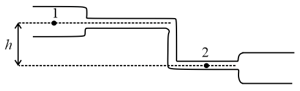
A steady flow of a liquid of density is shown in figure. At point , the area of crosssection is and the speed of flow of liquid is . At point , the area of crosssection is . Between the points and , the pressure difference is and the height difference is . The value of is
(Acceleration due to gravity )
A liquid of density flows smoothly through a horizontal pipe that tapers in cross-sectional area from to . The pressure difference between the wide and narrow sections of the pipe is . The rate of flow of liquid is _____ .
The area of cross-section of a large tank is . It has a narrow opening near the bottom having area of cross-section . A load of is applied on the water at the top in the tank. Neglecting the speed of water in the tank, the velocity of the water, coming out of the opening at the time when the height of water level in the tank is above the bottom, will be _____ .
[Take ]
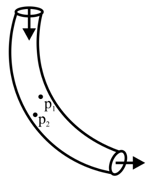
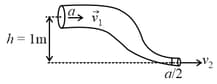
An ideal fluid of density , flows smoothly through a bent pipe (as shown in figure) that tapers in cross-sectional area from to . The pressure difference between the wide and narrow sections of pipe is . At wider section, the velocity of fluid is for _____ . (Given )
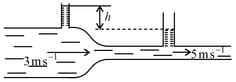
An incompressible liquid is flowing through a horizontal tube in streamline manner as shown in figure. The value of is (in meters)
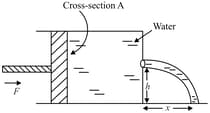
A liquid of density is forced out through a small hole by means of a piston of cross-section '', on which a force is applied. The flow is streamline. The liquid stream strikes the ground at a distance '' in front of the hole. The hole is in the middle of the right face and its height is '' above the ground. The expression for is:
What is the principle behind the carburator of an automobile?
"The fire fighters attach brass jets at the end of water pipes". Why ?
